Often called the “mother cannabinoid,” CBG is the compound from which many other cannabinoids, like CBD and THC, are formed. While it’s not as widely known as CBD, interest in CBG has been steadily growing thanks to early research suggesting it may support focus, gut health, mood balance, and inflammation relief.
But here’s the challenge: because CBG is relatively new on the market, there isn’t a universally accepted “standard dose.” Unlike over-the-counter painkillers or supplements that come with clear instructions, most CBG products leave dosage up to the user.
What’s the right starting point? How much is too much? And how do factors like weight, health goals, and product type affect how much you should take?
How Much CBG To Take
One of the biggest questions people have when first trying CBG is: “How much should I take?”
And honestly, there isn’t a single, scientifically confirmed dosage yet.
Unlike CBD, which has been studied more extensively, CBG research is still in its early stages. While some animal and small-scale human studies are promising, they don’t provide a one-size-fits-all answer for dosage.
That said, most of what we know comes from three places:
- Early clinical data — limited but growing. For example, one study found that a 20 mg dose of hemp-derived CBG helped reduce stress and anxiety without impairing alertness [1].
- Industry recommendations — many reputable CBD/CBG companies suggest starting around 5–10 mg per day and slowly increasing [2].
The safest approach is the classic cannabinoid rule: “start low and go slow.” Begin with a small amount (5–10 mg) and see how your body responds over several days. If you don’t notice benefits, increase gradually in 5 mg steps until you find your sweet spot.
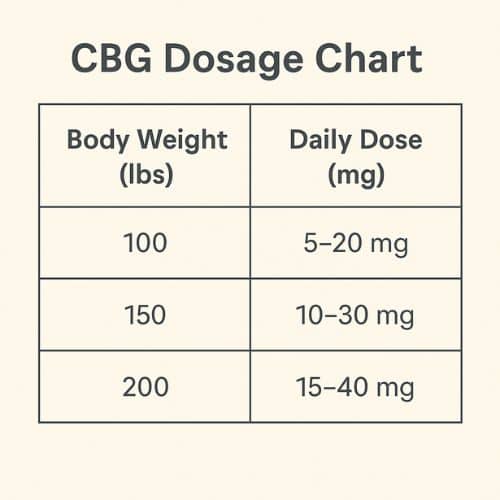
CBG Dosage Chart
CBG Dosage by Purpose
Because everyone’s body chemistry is unique, there’s no universal CBG dosage that everyone can follow. Many people adjust their intake depending on why they’re taking it and their desired effect. Here’s a list of evidence based, and user reported potential benefits of CBG.
1. Focus and Energy
Lower doses of CBG (around 5–15 mg per day) are often used for a gentle boost in focus and alertness. Many users find that smaller amounts are stimulating rather than sedating, making CBG a daytime option compared to CBD, which some say makes them too relaxed [3].
2. Stress and Anxiety Relief
For easing stress or mild anxiety, a mid-range dose of 10–25 mg daily is commonly reported. A recent small-scale human study showed that 20 mg of hemp-derived CBG helped reduce stress without impairing mental clarity [4].
3. Pain and Inflammation
When used for aches, inflammation, or recovery, people often lean into the 20–40 mg range. This aligns with anecdotal feedback as well as preclinical studies that found CBG may help reduce inflammatory markers in the gut and joints [5].
4. Gut and Digestive Support
Animal studies suggest CBD & CBG may benefit conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [6] [7]. While human research is lacking, early findings indicate that higher ranges could be more effective. For safety, users typically stay within 15–40 mg daily, starting lower and adjusting gradually.
What Is CBG and How It Works in the Body
CBG, or cannabigerol, is often called the “mother cannabinoid.” That’s because it’s the first cannabinoid the cannabis plant produces in significant amounts. As the plant matures, most of that CBG is converted into other cannabinoids like CBD, THC, and CBC. This is why CBG is usually found in much smaller quantities compared to its more famous cousins.
Unlike THC, CBG is non-intoxicating, meaning it won’t make you feel high. Instead, it interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is a network of receptors (CB1 and CB2), enzymes, and molecules that help regulate things like mood, sleep, pain, and immune response.
What makes CBG interesting is that it appears to bind more directly to both CB1 and CB2 receptors compared to CBD. This may explain why many people describe its effects as more “noticeable,” even at lower doses. Beyond the ECS, early research shows that CBG also interacts with:
- 5-HT1A serotonin receptors, which may influence mood and anxiety [8].
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, linked to pain perception and blood pressure regulation [9].
- TRP channels (transient receptor potential), which play a role in inflammation and temperature regulation [10].
CBG Products for Dosing
CBG Oils (Tinctures)
- How they work: Oils are taken sublingually (under the tongue) and absorbed directly into the bloodstream. This makes them one of the fastest and most efficient ways to feel CBG’s effects.
- Why people like them: Easy to adjust your dose drop by drop, and effects usually kick in within 15–30 minutes.
- Best for: Beginners who want control over their dosage and quicker onset.
- Recommended starting dose: 5–10 mg (about half a dropper, depending on strength) once or twice a day.
CBG Gummies
- How they work: Gummies and other edibles are absorbed through the digestive system, which means they take longer to kick in (30–90 minutes) but also last longer.
- Why people like them: Pre-measured servings make dosing simple, and they taste good.
- Best for: Consistent daily use, people who prefer not to taste the hemp flavor of oils.
- Recommended starting dose: 1 gummy (typically 10 mg), taken once daily. Increase slowly if needed.
CBG Capsules
- How they work: Similar to gummies, capsules are digested and absorbed slowly. They usually provide a steady, longer-lasting effect.
- Why people like them: Clean, precise dosing—what you see on the label is what you get every time.
- Best for: Users who want consistency and don’t want to fuss with droppers.
- Recommended starting dose: 1 capsule (usually 10–15 mg) daily.
CBG Vapes
- How they work: Inhaled CBG vapor enters the bloodstream almost instantly through the lungs. Effects are felt within minutes but wear off more quickly (about 1–2 hours).
- Why people like them: Immediate relief and easy dose control by how many puffs you take.
- Best for: Situational use (like sudden stress or pain), though not ideal for everyone due to lung health concerns.
- Recommended starting dose: 1–2 puffs and wait 10 minutes before taking more.
CBG Isolate
- How it works: Pure powdered CBG (usually 99%+ purity) that can be added to oils, foods, or homemade capsules.
- Why people like it: Maximum control over exact dosing, and no other cannabinoids or terpenes involved.
- Best for: Experienced users who want to fine-tune their dosing or blend CBG into custom routines.
- Recommended starting dose: 5–10 mg of isolate powder mixed into food, drink, or oil.
FAQ
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer because research is still limited. Most people start with 5–10 mg daily and adjust upward as needed. Some find relief in the 10–25 mg range, while higher doses (20–40 mg) are sometimes used for pain or inflammation.
CBG is considered well-tolerated, but taking too much may lead to side effects like drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, or low blood pressure. Always increase slowly and listen to your body.
Yes. Many people use CBG and CBD together for a balanced effect, since CBG is more energizing and CBD more calming. The two may complement each other, but you may need to experiment to find your best ratio.
Current evidence suggests CBG is safe for daily use when taken in moderate doses. However, because human research is still limited, it’s best to use lab-tested products and consult a healthcare professional if you’re on medication or have health conditions.
Bottom Line
Finding the right CBG dosage takes patience, experimentation, and a little self-awareness. Because research is still limited, there’s no official “standard dose”, but most people do well starting in the 5–10 mg range and gradually increasing until they find what works best.
The right amount depends on factors like your weight, metabolism, goals, and the type of product you’re using. Oils and vapes kick in quickly, gummies and capsules last longer, and isolates give you precision if you’re comfortable measuring your own dose.
The safest path is to start low, go slow, and track your results. Pay attention to how your body responds, and don’t rush into higher amounts. And as always, if you’re on medication or have existing health concerns, check with a healthcare professional before adding CBG to your routine.
- Beneficial effect of the non-psychotropic plant cannabinoid cannabigerol on experimental inflammatory bowel disease. (2013, May). ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006295213000543
- Brandrup, J. (2025, August 27). CBG vs CBD: Which Should I Choose? Neurogan. https://neurogan.com/blogs/news/cbg-vs-cbd-which-should-i-choose
- Cuttler, C., Stueber, A., Cooper, Z. D., & Russo, E. (2024a). Acute effects of cannabigerol on anxiety, stress, and mood: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, field trial. Scientific Reports, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-66879-0
- Cuttler, C., Stueber, A., Cooper, Z. D., & Russo, E. (2024b). Acute effects of cannabigerol on anxiety, stress, and mood: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, field trial. Scientific Reports, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-66879-0
- Garcia-Garcia, A. L., Newman-Tancredi, A., & Leonardo, E. D. (2013). P5-HT1A receptors in mood and anxiety: recent insights into autoreceptor versus heteroreceptor function. Psychopharmacology, 231(4), 623–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3389-x
- Giovannitti, J. A., Thoms, S. M., & Crawford, J. J. (2015). Alpha-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists: A review of Current clinical applications. Anesthesia Progress, 62(1), 31–38. https://doi.org/10.2344/0003-3006-62.1.31
- Harvard Health. (2022, September 26). Beyond CBD: Here come the other cannabinoids, but where’s the evidence? https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/beyond-cbd-here-come-the-other-cannabinoids-but-wheres-the-evidence-2021032322190
- The best CBG Dosing Guide: Achieving Optimal balance. (2025, April 23). CBD Alchemy. https://cbd-alchemy.com/en/blog/cbg-dosing-guide/
- Westmoreland, W. (2025, June 22). Is CBG good for pain? (Here’s what research says). Natural Ways CBD. https://www.naturalwayscbd.com/blog/cbg-for-pain/
- Wikipedia contributors. (2025, July 19). 5-HT1A receptor. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/5-HT1A_receptor









